The clean energy transition centers on eliminating fossil fuels from the larger economy, and buildings play a crucial role in this process. Globally, buildings are responsible for approximately 30% of final energy consumption and 26% of energy-related emissions.

Gradient Window Heat Pump's Role in the Clean Energy Transition: A Case Study in NYC
These emissions come from the use of carbon-intensive materials to construct buildings (embodied carbon) and the use of carbon-intensive fuels to run the day-to-day operations of buildings (operational carbon). Carbon-intensive fuels include coal, petroleum products, and natural gas, and they may be used onsite in furnaces or to run off-site power plants.
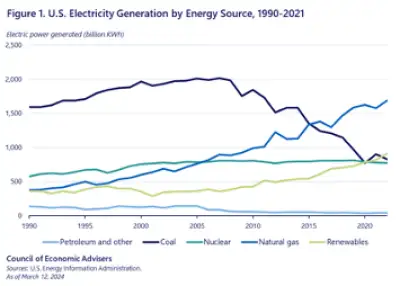
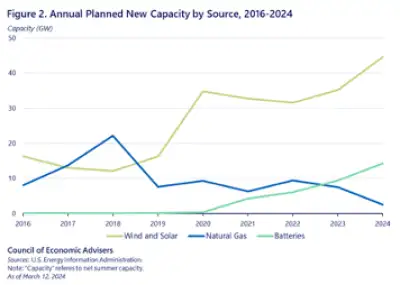
Passive design elements help improve efficiency, thereby driving down the amount of energy that’s needed to maintain the building’s typical operations. Meanwhile, converting older mechanical systems that run on oil or natural gas to newer, more efficient systems that run on electricity helps further reduce energy use, oftentimes to the point that buildings can be powered entirely by renewable energy sources like rooftop solar arrays. Any additional energy needs must come from the power grid. While it’s true that the grid may still be powered in part by fossil-fuels, the good news is that the percentage of energy generated by renewables has been climbing for the past 30 years (see Figure 1), and this trend is set to continue and perhaps even accelerate as grid-scale battery storage technologies become more sophisticated (see Figure 2).
Another trend that is set to accelerate is the use of heat pumps, which use electricity to heat and cool buildings and are extremely efficient. Due to their efficiency, wide-scale adoption of heat pumps can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions. In fact, a recent study published in the journal Joule found that converting all residential heating and cooling systems in the United States’ 65 million homes to heat pump systems would cut greenhouse gas emissions by 300-590 megatons per year, accounting for 36% to 64% of residential sector emissions and between 5% and 9% of economy-wide emissions for the U.S.
Additionally, the study found that the switch to heat pumps would result in energy savings of 31% to 47% for the average American home. When combined with building envelope improvements, the range increases to 41% to 52%. Other studies have found that the average American household can save up to $550 on their utility bills each year by converting to a heat pump system.

A Case Study in NYC
Gradient, an innovative heat pump manufacturer that created the original window heat pump, recently teamed up with the New York City Housing Authority to bring their window units to thousands of apartments across NYCHA’s 355-building residential portfolio.
An initial analysis of the in-field data collected by Gradient at NYCHA shows that the energy cost of the All-Weather 120V is less than half the cost of displaced fossil fuels.
The data, which was collected from 2023 and into 2024, shows that Gradient’s window heat pumps can reduce costs under a variety of conditions, including on NYC’s coldest winter day. The forecasted cost reductions were between 15% and 62% where Gradient heat pumps replaced natural-gas-fired steam heat, and between 51% and 78% where Gradient heat pumps replaced fuel-oil-fired steam heat.
While the level of cost savings varied, the implications are clear: Gradient heat pump performance at NYCHA forecasts extensive winter cost efficiency.
Ease of Installation
Returning to the Joule paper, the authors note that one of the primary obstacles to the more widespread use of heat pumps is the cost of installation. In addition to the costs of purchasing the air source heat pumps themselves, conventional heat pumps oftentimes require upgrades to electrical systems and new ductwork before they can be used. Labor costs also have to be factored into the equation.

With Gradient’s All-Weather 120V window heat pump, none of these issues are a concern. Unlike mini-split heat pumps, Gradient’s system is a single unit that can be installed without wiring upgrades, special tools, or specialized knowledge. Moreover, installation can be done without a permit, a technician, a contractor, or even a drill. All you need is a window, a standard 120V plug, and about 30 minutes. For multifamily owners, a building-wide conversion can occur over the course of a few days and without the need to displace tenants.
You can check out Gradient’s website to learn more about their All-Weather 120V window heat pump units. See how you can be part of the clean energy transition!